Internet of Things

Download our Tradetech Whitepaper
Accelerating trade digitalization to support MSME financing

Content
Internet of Things
IoT refers to the network of billions of physical “things” worldwide that are now connected to the internet and that collect and share data. These “things” are embedded with sensors, software and other technologies that allow them to collect and exchange data with other connected entities and systems.
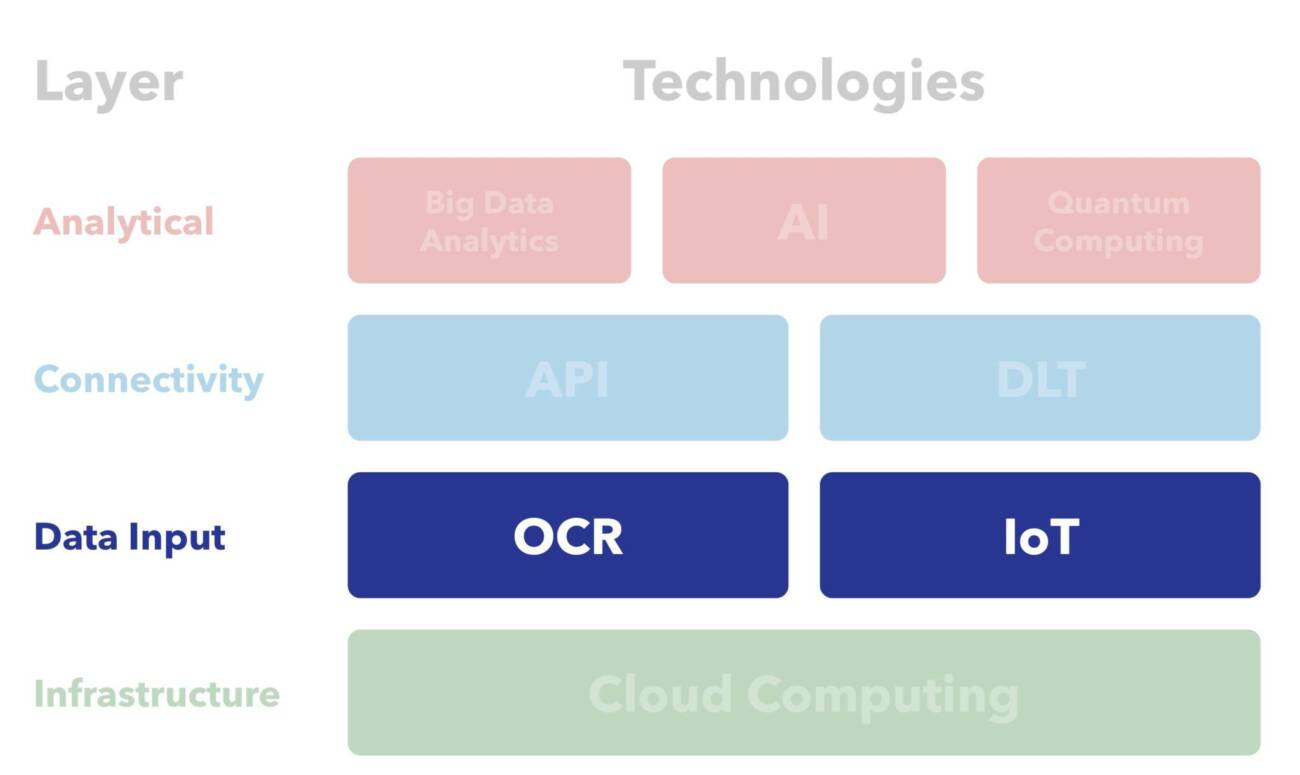
Potential benefits for MSMEs
The main benefit that IoT brings for MSME financing is that it adds transparency to and enables information to be communicated from and about each section of the physical supply chain, thanks to the data generated by a plethora of sensors and other devices; this will provide a higher sense of security for financial institutions to finance, which will benefit MSMEs. This added sense of security mainly stems from two features. First, IoT devices can operate as oracles for DLT-powered smart contracts, providing a powerful data input solution. Thus, events, reported by such IoT oracles, can be used as triggers to release portions of funds, mitigating the dissonance between sellers who want payment before shipment and buyers who want shipment before payment. Second is the ability to track goods while they are on a vessel or even in transit, meaning that the goods evaluation process will no longer require a physical presence. Sensors placed in containers can transmit vital information like temperature or CO2 levels, providing all parties with a sense of security between the shipping and the receipt of goods. Ultimately, more visibility into the trade lifecycle, will lead to better fraud prevention and greater participation from investors.
Use cases
As noted above, IoT is increasingly used to provide end-to-end visibility into the physical supply chain. Arviem, for example, a service provider for real-time cargo monitoring based in Switzerland, uses IoT technology to help clients with asset tracking, track-and-trace and supply chain visibility. Arviem has developed innovative supply chain finance services for goods in transit, leveraging IoT to monitor the location and condition of intermodal containers in real-time. essDOCS, a well-established company that provides paperless trade solutions, recently partnered with Swisscom and Linxens to develop their dTrack solution, which uses IoT technology to digitally track physical cargo and paper trade documents, distributing the document source data across the supply chain. This is done by making use of tamper-proof near-field communication chips attached to paper outputs, allowing dTrack to scan data and geo-tags across the supply chain. This IoT-based solution is used as a means to integrate the use of paper documents into trade finance by being able to digitally track them.
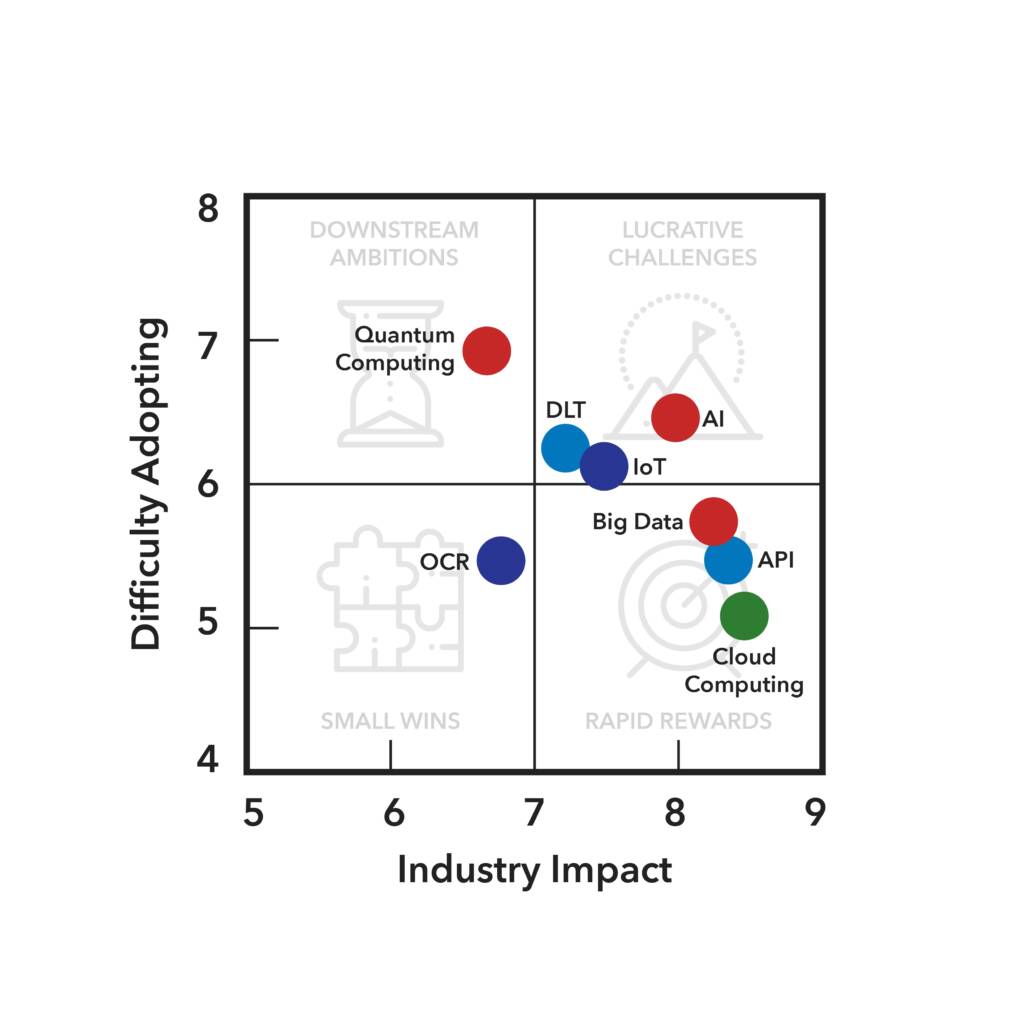
Addressing IoT challenges
For IoT, the largest challenges are related to using and understanding the data. Networks of IoT sensors can generate vast arrays of data. While this has the potential to be extremely valuable and provide useful insights, these insights cannot be put to practical use without robust analytics. To overcome this, firms need to be mindful of the internal procedural work that must be completed to ensure that staff, in conjunction with AI processes, are able to interpret and work with the new data effectively. These major internal challenges are clear next steps for IoT.
Another data issue relates both to data ownership and its legal admissibility in case of litigation. For example, it is unclear whether temperature data transmitted from an IoT sensor that depicts a spike in temperature above an agreed standard for a short period of time while, say, the vessel is crossing the equator, would constitute legal grounds for withholding payment on an otherwise unimpacted shipment. Overcoming this legal ambiguity requires regulatory work as well as the establishment of a common understanding and common approach to structuring and using data. These concerns, however, are not unique to IoT. Those seeking this change need to look beyond IoT-specific regulation and strive for a reform that will enable digitalization across the entire trade ecosystem.
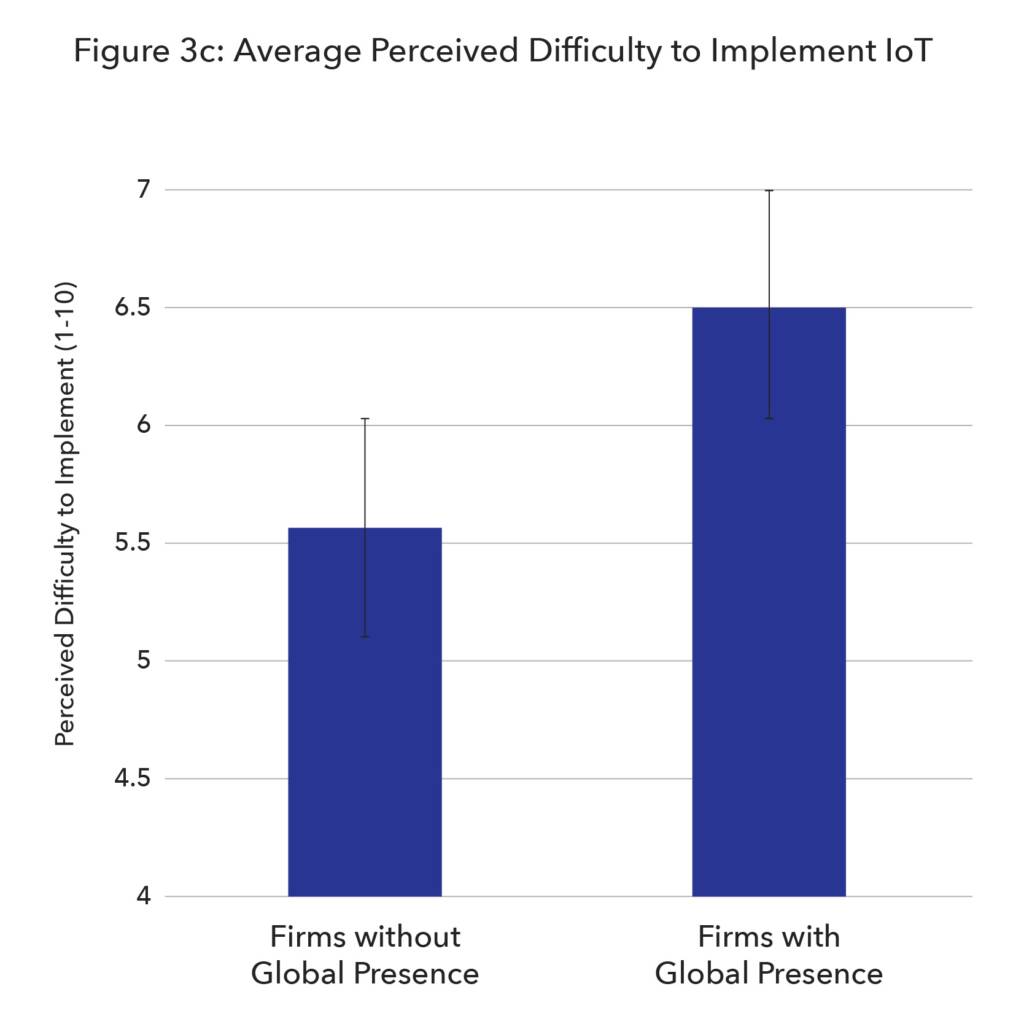
Beyond these external challenges, there are also challenges related to the potentially high costs of IoT networks. For many higher-priced goods, the additional cost of using an IoT device may be inconsequential, however for low-cost goods the cost of IoT can be prohibitive. Even in situations where the cost is not an immediate concern, there must still be enough perceived benefit to justify the expenditure. This is why ensuring tamper-proof devices is critical. Any form of tampering, malicious or unintentional, would render the IoT data worthless.
There are three primary security issues that arise with regard to IoT:
(1) intercepting and altering the data broadcast by the IoT device;
(2) tricking an IoT device into recording reporting data that are not true (for example, removing cargo from a crate and simultaneously replacing it with a boulder); and
(3) hacking into the IoT device to gain access to the connected system.
Addressing these challenges will help drive down costs relative to the perceived benefits of implementing IoT. Ensuring high levels of security is important, as are economies of scale, and the exploration of other connectivity-enabling technologies like 5G. The need for connectivity enablement exists since enhanced IoT requires ubiquitous networking which, in turn, implies the ability to connect everywhere.
At the end of the day, establishing clear roles and responsibilities for the supply chain participants and enabling the use of IoT data with ancillary participants like customs, ports, and freight forwarders will be critical. This is true regardless of whether future regulation and standardization will consider IoT to be an autonomous technology or simply an enabler or function of other autonomous technologies.
Publishing Partners
- Tradetech Resources
- All Tradetech Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences














