Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
A comprehensive Digital Trade Gap Assessment released by the World Bank provides an analysis of the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) framework across the Horn of Africa Initiative (HoAI) countries.
The Horn of Africa Initiative, a country-led programme, was launched in 2019 with the goal of promoting regional economic integration between five countries: Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, and South Sudan.
The HoAI includes 4 pillars:
- Regional infrastructure networks
- Trade and economic integration
- Building resilience
- Human capital development
The study, spearheaded by a team under the guidance of Alwaleed Fareed Alatabani, details the existing digital trade infrastructure and outlines strategic recommendations for enhancing ICT integration to boost regional trade.
This Digital Trade Gap Assessment aims to bridge the digital divide that hampers seamless trade across these nations.
Undertaken in two phases, the assessment involved direct engagements with key stakeholders, including government and private sector representatives across the five countries. The study methodically catalogued existing trade-related digital infrastructures and identified pivotal areas lacking in technological advancement.
Findings: A mixed landscape
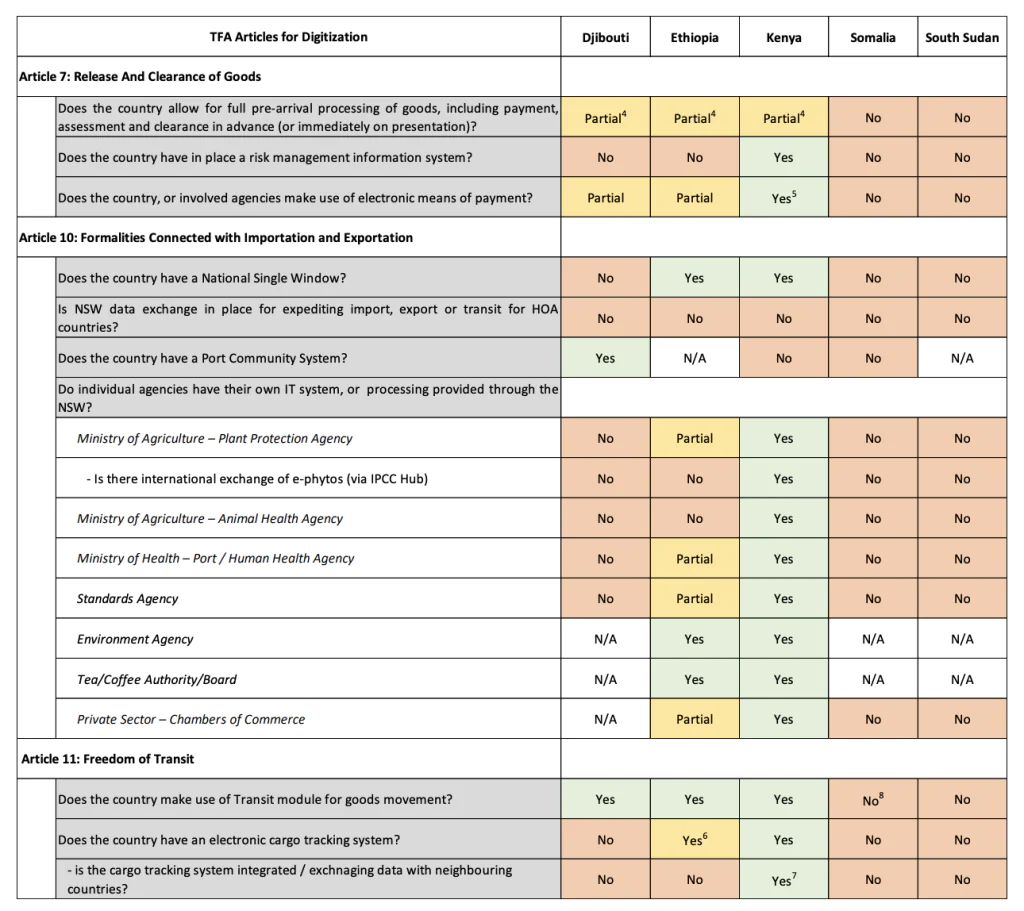
The World Bank’s report highlights a varied landscape of digital readiness among the HoAI countries:
- Kenya emerges as the frontrunner with robust digital trade systems, including an effective National Single Window (NSW) that facilitates streamlined trade processes.
- Ethiopia is catching up with significant initiatives like the Ethiopia Electronic Single Window (EESW) and ongoing efforts to enhance electronic cargo tracking systems.
- Djibouti and South Sudan show potential for growth despite the current limited digital trade infrastructure. Both countries are prioritised for immediate digital enhancements, including the development of trade information portals and e-cargo tracking solutions.
- Somalia presents a unique challenge with its nascent digital infrastructure, which requires foundational developments to support basic trade processes.

Gap analysis and strategic recommendations
The report highlights critical ICT gaps, such as the absence of comprehensive trade information portals in Djibouti, Ethiopia, and South Sudan, and the need for advanced data-sharing mechanisms across the region. To address these deficiencies, the World Bank recommends a series of digital interventions:
- Immediate establishment of Trade Information Portals in Djibouti, Ethiopia, and South Sudan is recommended to facilitate access to essential trade-related information and improve transparency.
- Development of National Single Windows in Djibouti, Somalia, and South Sudan could centralise and streamline trade processes, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with cross-border trade.
- Implementation of region-wide advanced data-sharing mechanisms would ensure efficient and secure cross-border data flow, enhancing the overall trade efficiency in the region.
The recommendations outlined in the report are designed not merely as patches to existing systems but as part of a strategic vision to foster a cohesive digital trade environment across the Horn of Africa.
These enhancements are expected to reduce trade barriers, lower transaction costs, and promote economic integration, which are pivotal for the region’s economic resilience and growth.
Future outlook
The World Bank concludes the assessment with a call to action for immediate and sustained interventions. It stresses the necessity for collaborative efforts involving regional governments, international donors, and private sector stakeholders to implement the recommended digital solutions.
The successful adoption of these measures would not only streamline trade processes but also enhance regional stability and economic development.
The full Digital Trade Gap Assessment report, including detailed findings and an exhaustive list of recommendations, is available through the World Bank’s official publication outlets. This document is intended to serve as a comprehensive guide for policymakers, international aid agencies, and stakeholders interested in enhancing the digital trade landscape in the Horn of Africa.
Read the full report here.