A few new technologies are now being leveraged by retail and high street banks in an attempt to maintain reduce operational costs, ensure security when trading, and facilitate the use of trade finance products. The International Chamber of Commerce recently published an industry report highlighting the benefits of latest technologies involved in global trading at large.
Trade finance digitalisation has typically been on products such as airway bills, bills of lading, certificates of origin, purchase orders, and invoices. This digitisation has helped in identifying and tracking customers, goods and the transport of goods, with records of processing and storing business data whilst complying with numerous regulations across different markets.
Banks are able to grow in a more agile way without bearing operational costs.
Key benefits of digitising trade finance:
- Reduction in operating costs
- Records of processing, storage of data securely, and non paper records might be more accurate and reliable
- Overall speed of transaction is reduced
- Lower overall costs for issuing a trade finance related loan
- Solid KYC / AML checks which are digitised and more instant
There’s a global shortage for trade finance provision
The inadequacy of trade finance solutions present in the market gets supported by the data by the Asian Development Bank and the World Trade Organization. About 7% of the trade finance requests from multinational companies are rejected, compared to about a 50% rejection rate when the applications come from SMEs. This equates to a global trade finance gap of around $1.5tn (in 2016).
As a result, organizations have reported writing off a huge proportion of global trade transactions.
New Technologies could help bridge the gap
In order to cope with the challenges posed by the complex nature of international trade and help facilitate navigation, a handful of technology companies and fintech companies have come forward to explore all commercial finance opportunities.
For instance, the collaboration between large corporations and banks with Traydstream helps in curbing expenses, risk mitigation, and digitalization of trade finance processes. A majority of those surveyed by the Asian Development Bank mentioned how beneficial this approach could actually be when it comes to lowering trade finance gap.
The technologies adopted and followed by Fintech companies are different from that of those that you use for FX trading. Forex traders seek the advantage of certain technical analysis for identifying their entry and exit points in the market. When it comes to analyzing potential pricing fluctuations for the future, traders use Bollinger brand analysis. Likewise, Fibonacci analysis can be used to determine support and resistance levels.
Digitization has been adopted by Fintech companies in many ways. One example is through blockchain and distributed ledger technologies, others include machine-learning automation, and optical character recognition (OCR). The latest blockchain technology has the power to ensure a much-enhanced security and processing speed for transactions between sellers and buyers as well as reducing associated banking costs. Ethereum has been identified as the main cryptocurrency that has the ability to disrupt Letters of Credit and various others.
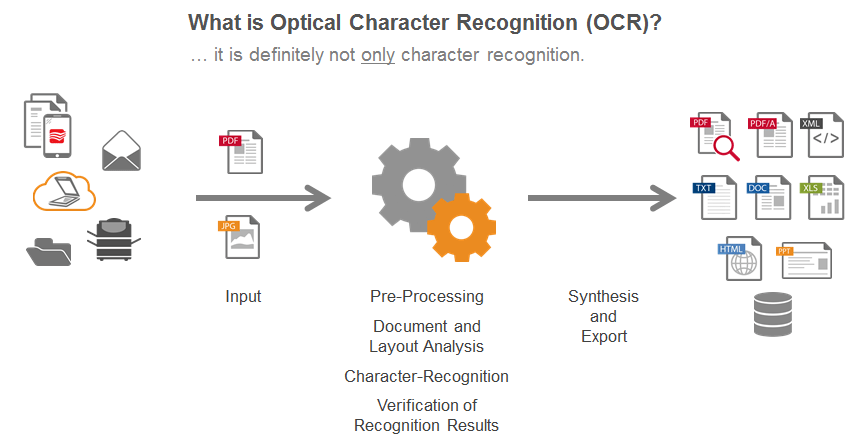
Source: Abby Technology: https://abbyy.technology/en:kb:tip:what_is_ocr
Banks achieve the promise of an effective cost-saving measure through automation, which is a combined outcome of various machine learning technologies and OCR. Although this concept is yet to be put to practice, it makes the most of the latest OCR technology. Sometimes, manual intervention is necessary for retrieving text material from paperwork and converting it to a format that’s fully legible to computers. OCR technology is mostly utilized for curbing the necessity for manual data entry and facilitating automation. A number of fintech companies resort to these initiatives and remain dedicated to meeting the end objective of developing a paperless trade environment globally. OCR is also useful in shipping and freight forwarding, particularly when suppliers and buyers work with cargo service providers to transport goods overseas.
The Digital Supply Chain Has a Long-term Impact
For all those businesses that are dealing in global trade, the big companies leading by example in terms of fintech are IBM, Traydstream and some other trade finance banks. According to an ICC report, the digital economy is likely to gain an additional $29 trillion during the next 10 years as a result of 350 million extra exporters being added to the network.
The entire world of international trade hasn’t yet experienced the impact of the digital supply chain in spite of an ever-increasing number of banks adopting the latest digitization technology during the last 2 years. In order to let these programs yield opportunity for global traders, all parties belonging to the supply chain must acknowledge such adoption universally at a time when every party is welcoming this as a move in the positive direction for creating a paperless future. Some exporters believe that we are less than three years away from trade finance transactions to be processed with the introduction of blockchain and other effective tools.
The Ultimate Benefit
Trade contributes some 3% of global GDP, and the increasing trade gap can be alleviated by the introduction of new technologies, including blockchain and ledger technologies, the digitalisation of paperwork in the shipping and banking industry and the emergence of AI in various technical elements of trading overseas.
What are your thoughts on which trends might infiltrate into trade first?