Understanding MT 734: advice of refusal

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get Started
ADVERTISEMENT
Contents
Understanding MT 734: advice of refusal
The Swift message type (MT) 734, “Advice of Refusal”, helps maintain the integrity of international transactions involving documentary credits.
Issuing and nominated banks use this message to communicate with the presenting bank, detailing the refusal of documents that do not comply with the terms and conditions of a documentary credit.
The MT 734 is vital for risk management, dispute resolution, and compliance adherence.
MT 734 format specifications
The MT 734 is designed to communicate a refusal of documents that, on their face, do not comply with the terms and conditions of the documentary credit.
It also provides instructions for disposing of these documents and can be used to claim refunds.
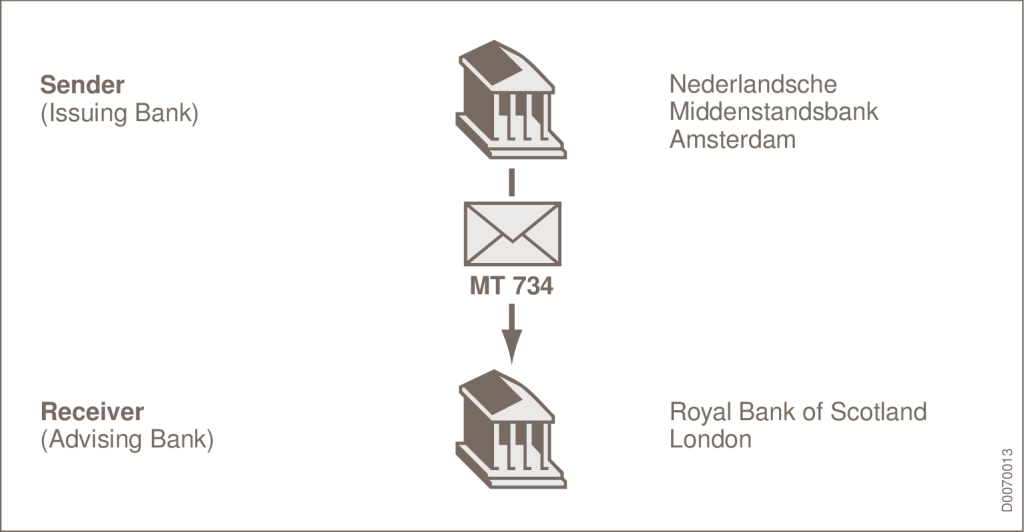
SOURCE: SWIFT
MT 734 key fields:
The MT 734 message has several key fields that ensure precise communication of the reasons for document refusal and subsequent actions required. These fields include:
- Fields 20 (Sender’s Transaction Reference) and 21 (Presenting Bank’s Reference): These fields offer a unique identifier for the transaction and link the refusal to the specific presentation by the presenting bank. Together, they are essential for tracking and establishing a clear reference point for the document presentation.
- Field 32A (Date and Amount of Utilisation): This field indicates the date when and the amount of the credit used. Understanding when and how much of the credit was drawn upon during the document presentation helps all parties gauge the transaction’s scope and the refusal’s implications.
- Field 77J (Discrepancies): Perhaps the most critical component of the MT 734, this field details the reasons for the document refusal. By clearly stating the discrepancies as they appear on the face of the documents, this field facilitates targeted communication between banks, enabling the presenting bank to address and potentially rectify the identified issues.
- Field 77B (Disposal of Documents): This field instructs the presenting bank on proceeding with the documents and whether they should be returned, held pending further instructions, or otherwise disposed of.
Why is the MT 734 important in international trade?
The MT 734 is important for global transactions as it:
- Ensures integrity of trade transactions: The MT 734 maintains strict adherence to the terms and conditions outlined in documentary credits by facilitating the formal notification of document refusal due to discrepancies.
- Promotes efficient dispute resolution: The detailed advice of refusal, including specific discrepancies and instructions for document disposal, allows for a more structured and efficient approach to resolving disputes between parties involved in the trade.
- Supports compliance and risk management: The MT 734 helps mitigate risks associated with documentary credit transactions by clearly communicating non-compliance and facilitating the appropriate handling of refused documents.
- Facilitates transparent communication: The structured format of the MT 734 ensures that all parties involved in a transaction are fully aware of any issues with documents presented under a documentary credit, promoting transparency and accountability.
Who uses MT 734, and why?
Users
Issuing and nominated banks are the primary users of MT 734 in the context of documentary credits.
These entities use the message to formally notify the presenting bank of the refusal of documents due to non-compliance with the credit terms and conditions.
Purpose
The MT 734 ensures that discrepancies are communicated and addressed, upholding the standards required for international trade financing.
The message also facilitates the orderly resolution of disputes and the proper handling of refused documents.
Potential issues and technological advancements
Challenges
- The complexity of discrepancy identification: Identifying and detailing discrepancies in trade documents can be complex and requires a high level of expertise, making the process susceptible to errors and misunderstandings.
- Operational delays: The refusal of documents can lead to delays in the transaction, affecting the timely completion of trade operations and potentially leading to financial losses for the parties involved.
Advancements
- Digitalisation and automation: Advances in digital document handling and automation technologies are streamlining the discrepancy identification process, reducing errors, and speeding up the communication of refusals.
- Blockchain and smart contracts: Integrating blockchain technology and smart contracts in trade finance can enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. These technologies could potentially automate compliance checks, minimising the likelihood of document refusal.
The MT 734 is a vital instrument in international trade finance that provides a structured mechanism for advising the refusal of documents under documentary credits.
Its importance lies in its ability to facilitate clear communication, ensure compliance with trade terms, and efficiently resolve discrepancies.
As the trade finance landscape evolves, technological advancements promise to further enhance the functionality and effectiveness of the MT 734 and similar message types.
- More articles on SWIFT Messaging Types
- Messaging Types Resources















