Taking security over assets

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContents
A security is a negotiable financial instrument which has a monetary value. Securities over assets are used to secure a transaction. When entering into a credit agreement, the lender will seek to get the loan money back. For this purpose, various securities can be taken. In English law, four main types of security are mortgages, charges, pledges, liens.
Mortgages – The borrower offers their property as security for a loan, giving the lender the right to reclaim the collateral in the event of a default.
Charges – As sort of security interest established over particular assets, giving the creditor the authority to sell the charged assets in order to pay the debt in the event of default.
Pledges – Security arrangement in which the borrower gives the lender custody of an asset as security, with the understanding that the asset would be restored after the debt is paid back.
Liens – Legal claim or right that enables a creditor to keep control of a debtor’s possessions until the full amount of the debt is paid.
Several benefits are granted to the lender when taking security from a borrower.
First, they have rights against the assets of the borrower, mainly in the form of a right to ownership. In cases where the borrower fails to perform its obligations under the loan, the lender will be able to use these rights to take possession or sell the asset to repay the loan.
Secondly, taking a security gives the lender a priority over other lenders in receiving payment.
In sum, taking a security over an asset constitutes an efficient way for the lender to recover a claim against the borrower.
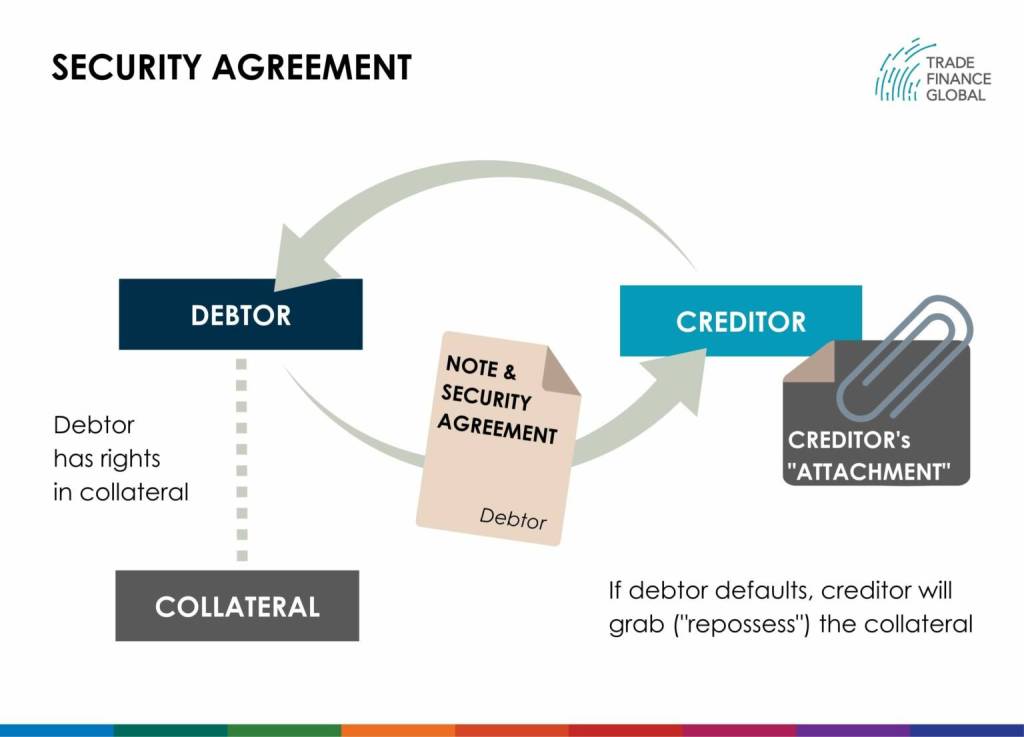
FIG.1: A security agreement transfers the debtor’s (borrower) rights over its collateral to the creditor (lender).
Perfection of a security
Once a security has been created, it becomes binding between the lender and the borrower. However, this security interest may not be binding as regards third parties.
The perfection of a security relates to the process undertaken by the lender whereby a security interest acquires the optimal protection against third parties. By that way, the security takes priority over unperfected securities related to the same asset. Different possibilities for a security interest to be perfected are available:
By possession
Possession is a concrete indication that the secured lender is asserting a claim on the asset. The possession can also be ‘constructive’, for instance where the lender is in possession of a title document. This method of perfection will only be possible where the secured asset is a tangible property such as diamonds.
By registration
Security can also be perfected by way of registration. Under English law, the most common process is to register the security at Companies House. This method of perfection exists for most types of security, including:
- Security over land
- Company charges: on property or on book debts
- Security over any intellectual property
- Security over a ship of aircraft
By virtue of the Companies Act (2006) in its Section 859A, the period allowed to register newly created securities is within 21 days of their creation. Perfection by registration at Companies House guarantees the validity of the security and its priority over later security on the same asset.
By giving notice
The lender will have recourse to this method where the security has been taken over intangibles assets such as debts. In English law, notice shall be given following the rule in Dearle v Hall.
Pursuant to this rule, priority of assignment of debts depends upon the date of notice given to the borrower who owes the debt. In doing so, the lender will ensure that its security has priority over other securities subsequently created over the same asset.
The importance of giving notice arises in cases where a second security is created, since the aforementioned rule is also a rule of priority. If the second lender gives notice to the borrower before the first lender had given one, this second security will take priority over the first, given that the second lender did not know about the original assignment.
In brief, the first lender to give notice to the borrower will have prior claim over the asset, irrespective of the order in which the securities were granted.
However, the rule in Dearle v Hall can be defeated in three circumstances:
- When the borrower is a company
- When the security of the first lender is registered at Companies House
- When the second lender could reasonably be expected to have searched that register
It should be noted that, in these cases, the first lender still needs to give notice to the borrower.
Priority of a security
Priority is one of the leading benefits of taking security over an asset. Issues about priority arise when competing security interests are taken over the same asset.
The priority rules refer to the order in which lenders with a security will be paid out of the proceeds of the assets at issue. In other words, it means priority of payment regarding the asset which has been secured.
In cases where proceeds of the security are not sufficient to pay all the secured lenders, priority issue is of critical importance since some of them may not recover the amount loaned to the borrower. The highest is the rank of the lender, the likelier they are to be able to claim its rights over the asset and get paid back.
The general rule concerning security is that a lender with a security interest in an asset takes priority over subsequent security interests in the same asset, also called ‘first in time’ principle. However, exceptions to this rule exist:
- A legal security interest takes priority over earlier equitable security interest in the same asset if certain conditions are met: the later secured lender has no notice of the earlier security interest and gives value for its legal interest.
- The priority of competing security interests regarding certain intangible assets, such as debts or rights under a contract, is determined based on the dates on which the notice of the security interests has been provided to the borrower.
- In case of security interest being registered in related asset registries, priorities between competing security interests will be determined by the date of registration.
- Fixed charges take priority over floating charges.
The Mortgage Credit Directive, officially known as Directive 2014/17/EU on Credit Agreements for Consumers Relating to Residential Immovable Property, has been placed into effect by the European Union.
This Directive specifies particular provisions with respect to the assignment of Credit Agreements with Residential Immovable Property as Security. When a client’s mortgage loan is moved to or allocated to another company, it ensures that they are protected and informed. The regulation specifies precise standards for consumer notification and information disclosure throughout the assignment process.
Additionally, the way receivables are assigned may be radically changed by the advent of blockchain technology. By leveraging distributed ledger technology, blockchain improves security, transparency, and transaction traceability. Smart contracts built on blockchain technology can automate the assignment process, guaranteeing that all parties follow specified guidelines and a smooth transfer of receivables.
- International Trade Law Resources
- All International Trade Law Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences















