Risks & Limitations of Correspondent Banking

Contents
What are the risks of correspondent banking?
Correspondent banking involves multiple parties, including correspondent banks, issuing banks, and other intermediaries, each facing different risks.
Correspondent banks, for example, must consider credit risk, reputation risk, compliance risk, and operational risk. Inadvertently being involved in an illegal transaction due to inadequate compliance practices can lead to lasting reputational damage and severe financial penalties.
But it is not just banks that need to be mindful of the potential risks. Other intermediaries, such as payment processors and clearinghouses, face operational and reputational risks if they are associated with illegal or unethical activities.
In some cases, these third-party operational risks would have widespread consequences for the entire industry if they materialised. For example, if a payment processor experiences a system failure, it can result in delayed or failed transactions, causing significant trouble to the financial system.
While individual firms are only indirectly involved in the correspondent banking system, they too, can face considerable risks, including delayed or failed transactions, higher costs, and potential reputational damage.
Another potentially devastating impact for firms is financial exclusion.
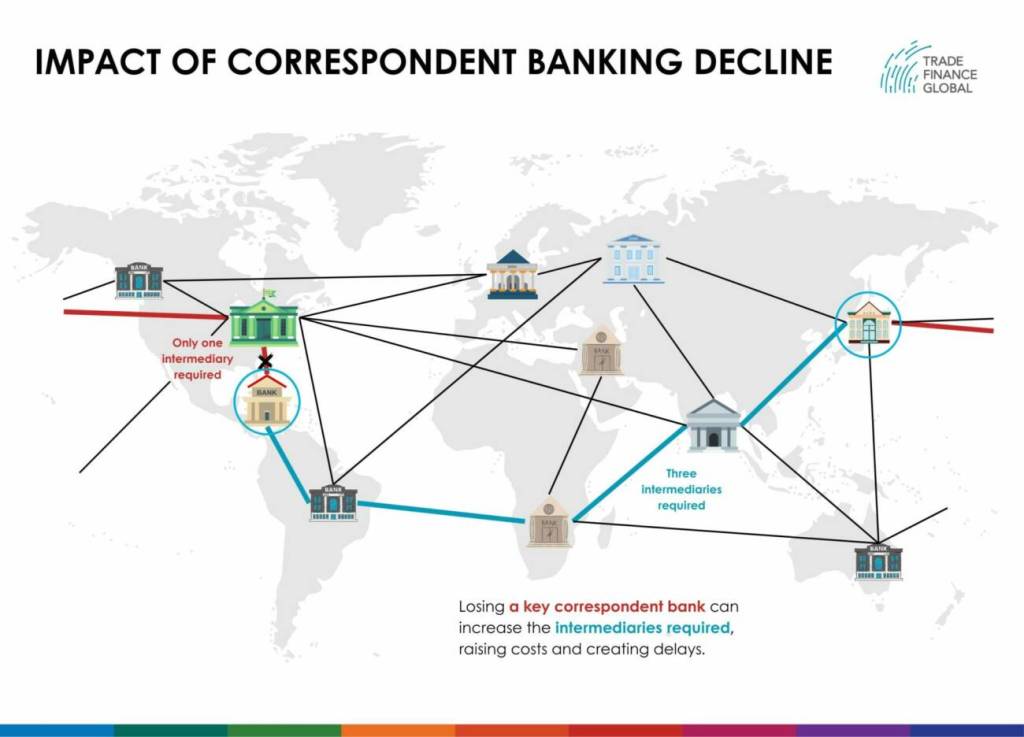
If banks in developed nations perceive higher risks in specific regions or sectors, they may limit their correspondent banking relationships in that region. For firms in those often undeveloped regions, this reduces their access to financial services and can make it more difficult to trade on the global market.
In recent years, increased de-risking in the Caribbean has led to sharp price increases and time delays for firms trading abroad.
What is de-risking and its implications for banks?
De-risking is a process by which banks reduce or terminate relationships with customers, counterparties, or regions that are deemed to be high-risk. This can be in response to various factors, including regulatory pressure, reputational concerns, or concerns about financial crime.
While de-risking may be deemed necessary in a bank’s internal boardroom, the practice can have wide-reaching implications for the bank itself and the global economy more generally.
For example, de-risking can damage a bank’s reputation if it is seen as unfairly targeting specific customers or regions.
Furthermore, those businesses and individuals in the de-risked regions will be at a greater risk of financial exclusion since the reduction in correspondent relationships can lead to a broader reduction in financial services.
Overall, de-risking can have significant implications for banks – including reduced revenue, increased costs, and reputational damage – and the broader economy – including financial exclusion.
Banks must carefully balance managing their risk exposure with providing access to financial services and supporting economic growth.
This requires a comprehensive and integrated approach to risk management, including robust compliance measures, effective due diligence, and ongoing monitoring and reporting.
How do you manage the risks of correspondent banking?
To manage the risks of correspondent banking, parties involved should implement robust risk management policies and procedures.
Banks should conduct rigorous and ongoing due diligence on partner institutions to assess their reputation, financial stability, and compliance with KYC, AML, CTF, and other regulations
They also need to continually monitor transactions for suspicious activities – being sure to report any unusual transactions to the relevant authorities – and implement controls to help safeguard against these risks. These processes will be aided by investment into enhanced IT infrastructure and other digital tools.
Strong governance practices – both internal in the form of documents, chains of command, and processes and with external regulators and partners – are also a key aspect that can help to mitigate correspondent banking risks
Managing the risks of correspondent banking requires an integrated approach, but by investing the time and effort to implement these measures, parties engaged in correspondent banking can reduce the risk of financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
As the industry continues to digitise, stakeholders must collect and maintain strong compliance data records.
Why is compliance data important in banking transactions?
Compliance data is essential in banking transactions for multiple reasons.
By collecting and analysing compliance data, banks can identify suspicious activities and take appropriate measures to safeguard against financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorist financing.
Compliance data can help them meet their various regulatory requirements by providing evidence of their compliance efforts and helping them identify and address any gaps in their procedures.
In addition to this regulatory lens, collecting compliance data can help boost a bank’s reputation by demonstrating its commitment to preventing financial crimes. This can be particularly important for banks operating in high-risk jurisdictions or subject to compliance-related penalties or sanctions.
If these external factors are not enough, the value of data – particularly as the industry enters its information age – can provide insights to help banks make better decisions related to business development and customer relations. For example, compliance data can help banks identify high-risk customers or jurisdictions and adjust their business strategies accordingly.
By collecting and analysing compliance data, banks can better understand and manage the risks associated with their operations, which can ultimately help them protect their customers and the broader financial system.
Correspondent Banking Partners
s
- Correspondent Banking Resources
- All Correspondent Banking Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences



















