Correspondent Banking Relationships

Contents
What’s the relationship between correspondent banks and respondent banks?
Correspondent and respondent banks are two types of banks that engage in correspondent banking relationships to facilitate international financial transactions.
Correspondent banks are the financial institution that provides banking services on behalf of another financial institution (known as the respondent bank). In most cases, correspondent banks offer their respondent banks services such as wire transfers, foreign currency exchange, and trade finance. These banks often have extensive networks and relations with other financial institutions around the world, which allows them to facilitate transactions in different currencies and jurisdictions.
A respondent bank, then, is the financial institution that receives banking services from a correspondent bank. Respondent banks typically maintain accounts with correspondent banks – (referred to as either a nostro or vostro account, depending on which party is referring to it) – and use the correspondent’s services to facilitate international transactions for their customers.
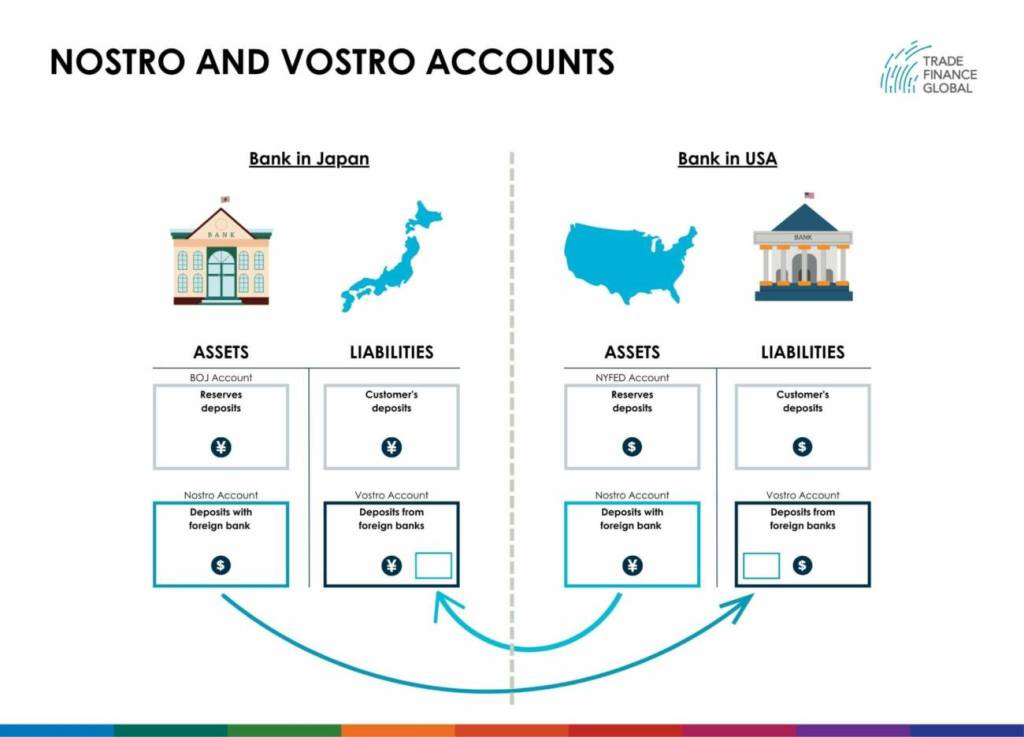
What is nostro and vostro?
Nostro and vostro are terms used in the context of correspondent banking relationships.
Nostro refers to an account that a bank holds in a foreign currency with another bank, while vostro refers to an account that a bank holds in its own currency on behalf of another bank.
For example, if the MUFG Bank in Japan holds an account in US dollars with Morgan Stanley in the USA, this would be referred to as a nostro account for MUFG and a vostro account for Morgan Stanley.
By maintaining nostro and vostro accounts, banks can reduce the time and cost involved in processing international transactions and improve the efficiency of their operations.
What is the difference between a correspondent bank and an intermediary bank?
While correspondent banks and intermediary banks are both involved in facilitating international financial transactions, there are some critical differences between the two.
As we’ve learned, a correspondent bank is the financial institution that provides banking services on behalf of another financial institution in a different geographic location. On the other hand, intermediary banks are financial institutions that act as a mediator between two other financial institutions involved in a transaction.
Intermediary banks may be used to facilitate transactions in situations where the correspondent bank is unable to process the transaction directly or where there are multiple correspondent banks involved in the transaction.
In some cases, correspondent banks may also act as intermediary banks, depending on the specific transaction and banking relationships involved. However, not all intermediary banks are correspondent banks.
Correspondent and intermediary banks play essential roles in facilitating international financial transactions, but they are often not the only banks involved in the process – there are also beneficiary banks.
What is the difference between correspondent bank and beneficiary bank?
A correspondent bank and a beneficiary bank are different types of banks that play different roles in international financial transactions.
While correspondent banks administer banking services on behalf of their respondent banks, the beneficiary bank is the financial institution that ultimately receives the funds or assets being transferred.
For example, imagine a Canadian mining company that banks using TD Bank is selling 100,000 Canadian dollars worth of precious metals to an Australian jeweler that banks with Commonwealth Bank.
To facilitate this transaction, the Australian jeweller’s bank would leverage its nostro account with its correspondent banking partner in Canada, which is the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC). RBC would then send the required funds to the mining company’s account with TD Bank, and the transaction can be completed.
In this example, Commonwealth Bank is the respondent bank, RBC is the correspondent bank, and TD is the beneficiary bank.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of correspondent banking relationships?
Correspondent banking relationships offer several advantages and disadvantages to financial institutions. Some of the key advantages include:
- Increased global reach: By establishing correspondent banking relationships, financial institutions can provide their services to customers in countries where they do not have a physical presence, including those in developing countries.
- Access to local currency and payment systems: The correspondent banking system allows cross-border transactions to be processed in the local currency and through local payment systems. This is a critical function given that most international trade transactions – regardless of the nations involved – are conducted in the United States Dollar.
- Reduced cost and risk: By leveraging the expertise and infrastructure of correspondent banks, financial institutions can reduce the cost and risk associated with processing international transactions.
- Improved compliance: Correspondent banks are subject to strict regulatory requirements and compliance standards. By partnering with a reputable correspondent bank, financial institutions can improve their compliance with regulations and reduce the risk of fines or penalties.
While these advantages exist, there can also be several disadvantages to correspondent banking, including:
- High fees: Correspondent banking relationships can involve high fees, particularly for small and medium-sized financial institutions.
- Complexity: Correspondent banking relationships can involve multiple parties, making it difficult to manage risks and ensure compliance.
- Reputational risk: Correspondent banking relationships can expose financial institutions to reputational risk if their correspondent banks are involved in illegal activities or sanctions violations.
- Dependence on correspondent banks: Financial institutions may become dependent on their correspondent banks for critical services, which can create operational risks if the correspondent bank experiences financial difficulties or other issues. Several regions worldwide are also experiencing a general decline in correspondent banking relationships, to the detriment of economic progress.
Successful due diligence checklist
Due diligence is a necessary process that financial institutions should undertake before entering into correspondent banking relationships.
There are several things that potential partners should investigate during the due diligence process. While this is not an exhaustive list, some such items include:
- Background checks: Conduct background checks on a prospective correspondent bank to identify any red flags, such as sanctions violations or legal issues.
- Financial performance: Review the financial performance of the prospective correspondent bank to determine if it is financially stable and can meet its obligations.
- Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing: Review the prospective correspondent bank’s anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing policies and procedures to ensure they are robust and effective.
- Technology and infrastructure: Evaluate the technology and infrastructure of the prospective correspondent bank to ensure that it is up-to-date and can support the financial institution’s needs.
- Contracts and agreements: Review any contracts and agreements with the prospective correspondent bank to ensure they are clear, comprehensive, and adequately protected.
- On-site visits: Consider conducting on-site visits to the prospective correspondent bank to gain a better understanding of its operations and culture.
- Ongoing monitoring: Establish an ongoing monitoring process to ensure that the correspondent banking relationship continues to meet the financial institution’s needs and remains compliant with regulations.
Correspondent Banking Partners
s
- Correspondent Banking Resources
- All Correspondent Banking Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences



















