History of Blockchain


Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get startedContent
The blockchain is regarded by some as the most revolutionary technological innovation since the dawn of the internet; the foundation of ‘Web 3.0’, here to usher in the future of the internet.
Most people know blockchain as the technology behind Bitcoin – and this was indeed its first application – but since then, several innovations in the system have allowed blockchain to spread far and wide.
The blockchain system is now democratizing and transforming all kinds of industries, from healthcare to trade finance. In fact, we’ve already written about how blockchain is changing the supply chain here.
But before we try to predict the future of blockchain, it’s important to first delve into it’s past. Below, TFG has prepared a timeline of all the major events in the history of blockchain to enable you to learn more about how this revolutionary system has developed over time
The 5 Major Blockchain Innovations
In just 10 years, there have been five major innovations in the blockchain system that have created huge breakthroughs. These are:
- The invention of Bitcoin
- The separation of blockchain from Bitcoin
- The invention of Smart Contracts
- The transition to Proof-of-Stake mining
- The focus on blockchain scaling solutions
Let’s look at each of these in more detail.
The Invention of Bitcoin
Blockchain began with a man named Satoshi Nakamoto, who invented Bitcoin and brought blockchain technology to the world back in 2009. Bitcoin aimed to be a viable alternative to fiat currency. A secure, decentralised, global currency that could be used as a medium of exchange. In the first year, the currency was worth $0. Now, it has a total market capitalization of $126 million.
Nakamoto built on the foundations laid by those who came before him. In the pre-bitcoin years, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta had already begun work on a cryptographically secured chain of blocks but the first blockchain wouldn’t be truly conceptualised until Nakamoto’s invention in 2008.
Following the release of the Bitcoin whitepaper, it was made open source, which allowed anyone with an interest to build on the existing code. This lead to the release of many so-called ‘altcoins’ – cryptocurrencies which sought to improve on Bitcoin. Some notable early adopters of the Bitcoin code were Litecoin and Namecoin.
Blockchain Separates from Bitcoin
A few years after the release of Bitcoin, developers began to see the far-reaching potential of Blockchain and began to explore its uses outside of the cryptocurrency realm. Before this, blockchain and Bitcoin were often thought of as the same thing, when in reality, Bitcoin is simply an application built with Blockchain.
Blockchain itself is a decentralised, distributed ledger designed to record transactions permanently without third-party authentication. This makes it useful for any exchanges that could benefit from increased transparency, speed and decentralisation.
This realisation spurred huge investment and research into blockchain and, around 2014, attempts to repurpose the blockchain for use in applications for healthcare, insurance, supply chains, voting, and more began in earnest. As of 2017, around 15% of all banks were using blockchain technology in some capacity.
Smart Contracts
The next great innovation in blockchain technology came from a man named Vitalik Buterin. In 2013, he founded Ethereum – a cryptocurrency which has since grown to become the second largest on the market by market capitalisation.
He designed Ethereum to be more than just a cryptocurrency and wanted it to be used as a tool to build decentralised blockchain applications. He included a feature known as ‘smart contracts’, which provided a way for the blockchain to be used to exchange anything of value directly, without any middlemen.
Before this, only cryptocurrency tokens like Bitcoins could be exchanged. Ethereum smart contracts allow other assets, like bonds, loans, products or services, to be exchanged. During an exchange, they hold these assets in escrow until a predetermined set of criteria are met before releasing them to both parties.
Smart contracts are increasingly being used by huge corporations, such as Microsoft and UBS, to cut down on costs and save time.
Proof of Stake Mining
The next big shift in the way blockchain technology is used came when developers of cryptocurrencies like Ethereum moved away from proof of work mining in favour of proof of stake mining.
Mining is the process whereby new blocks are created and transactions are verified. This is done via computer power in a proof of work system. Miners use their computing power to solve a complex mathematical problem which verifies the transaction. They’re incentivised to do this via a reward system where they earn a share of fees or generate new tokens. Those with the largest computational power can mine the most coins.
Proof of work and proof of stake are both different algorithms for this mining process. Proof of stake seeks to improve upon issues of cost and energy consumption identified in the proof of work model by attributing mining power based on stake as opposed to computational power.
Blockchain Scaling Solutions
One of the limitations of the blockchain at present is its scalability. As transactions have to be processed by all the computers in the blockchain network, transaction speeds can be slow.
There are developers working on solutions to this problem which may involve determining a minimum number of computers that are needed to verify transactions without compromising security.
Other cryptocurrencies have already partially solved this problem and offer much faster transaction speeds than Bitcoin.
Market History
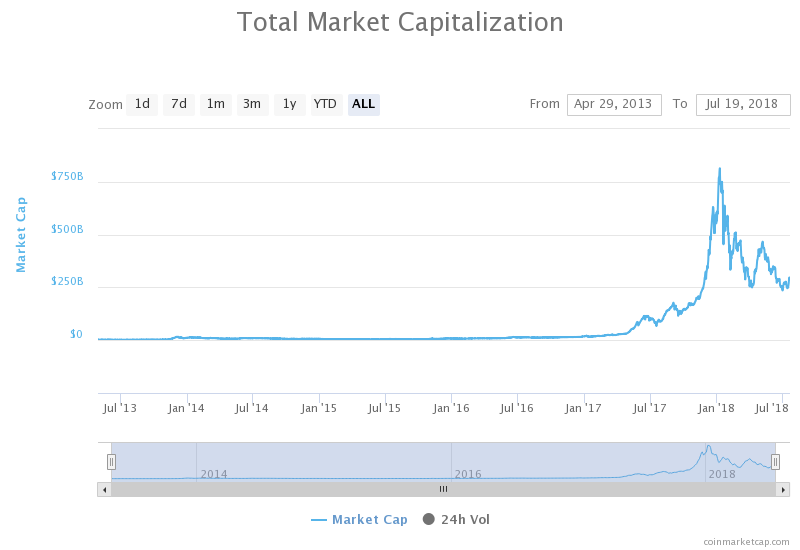
Since 2013, there have been several periods of rapid growth in the cryptocurrency market. Cryptocurrencies have proved to be extremely volatile, and though the market shows a general upward trend over time, there have been long periods of little growth and the biggest price gains have occurred in very short time periods.
Below is a graph illustrating the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies between April 2013 and July 2018.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blockchain#History
https://hbr.org/2017/02/a-brief-history-of-blockchain
https://www.wired.com/story/guide-blockchain/
https://parameter.io/history-of-cryptocurrency/
Publishing Partners
- Blockchain & DLT Resources
- Cryptocurrency Resources
- All Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Resources
- Conferences















