Understanding MT 707: Amendment to a Documentary Credit

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get Started
ADVERTISEMENT
Contents
The MT 707 plays a crucial role in the fluid dynamics of international trade finance, serving as a communication tool for amending the terms and conditions of a documentary credit. This guide aims to unpack the MT 707 format, shedding light on its users, purposes, potential challenges, and the advancements shaping its future use.
The MT 707 message, utilised for amending a documentary credit, comprises various fields that facilitate precise modifications to the credit’s terms. Here’s a closer examination of its format specifications and some key fields:
MT 707 format specifications
- Scope: The MT 707 allows issuing banks to communicate amendments to advising banks, which can further relay these changes to other relevant parties. It is instrumental in updating the terms and conditions initially set forth by the documentary credit.
- Functionality: This message type ensures that any changes, whether adding, modifying, or deleting terms, are clearly communicated and acknowledged by all involved parties.
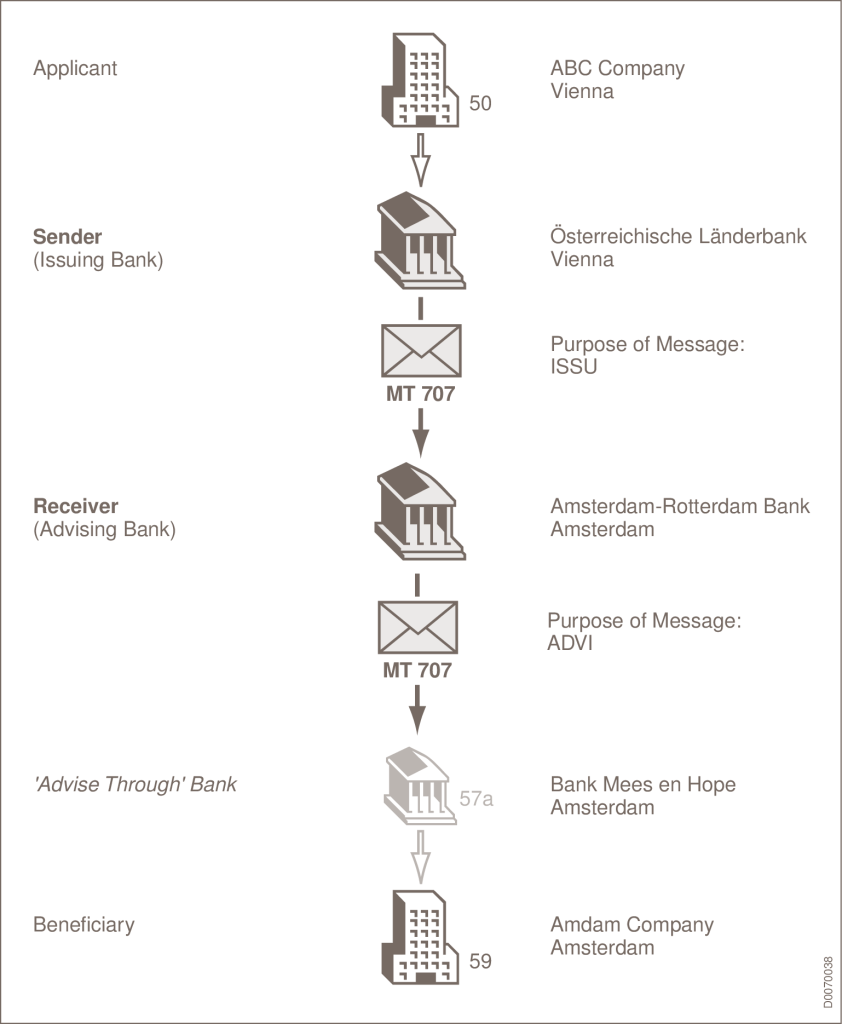
SOURCE: SWIFT
Key fields explained
- 27 – Sequence of Total & 20 – Sender’s Reference & 21 – Receiver’s Reference: These fields ensure the amendment’s proper sequencing and provide unique identifiers for both the sender and receiver, facilitating accurate tracking and referencing of the amendment.
- 31C – Date of Issue & 26E – Number of Amendment & 30 – Date of Amendment: Outline the original issuance date of the credit, the specific amendment sequence, and the date on which the amendment is made, crucial for historical tracking and validity of the changes.
- 22A – Purpose of Message & 32B/33B – Increase/Decrease of Documentary Credit Amount: Identify the amendment’s intent and detail any adjustments in the credit amount, ensuring clear communication of the amendment’s nature and financial impact.
- 59 – Beneficiary: Any changes to the beneficiary’s details are specified here, ensuring accurate identification.
Network Validated Rules
- C1: At least one field must be present after field 22A to validate the amendment’s content, ensuring that the amendment’s details are properly conveyed.
- C2 & C3: Specify that either an increase or decrease in the documentary credit amount can be stated (but not both simultaneously) and that either field 50B (Non-Bank Issuer) or field 52a (Issuing Bank) must be present, enhancing clarity on the issuing entity and the amendment’s financial aspects.
- C4: Dictates the exclusive presence of either the latest date of shipment (44C) or shipment period (44D), avoiding conflicting information on shipment timelines.
Usage rules
- Comprehensive amendments: When details exceed the MT 707’s capacity, additional information must be transmitted via MT 708 messages, allowing for an exhaustive presentation of changes.
- Operative nature: The MT 707, along with any associated MT 708s, forms an integral part of the documentary credit, affirming the amendments as part of the binding terms unless specified otherwise.
- Consistency and clarity: Amendments must be precisely defined to avoid repetition and ensure no conflicting information is presented across related messages.
Who uses MT 707 and why?
The users of MT707
Banks and financial institutions across the globe employ the MT 707 for amending documentary credits in international trade. The issuing bank initiates amendments, which are then communicated to advising or transferring banks. This message type is pivotal for importers, exporters, and their financiers, ensuring that documentary credits accurately reflect the terms agreed upon by all parties involved.

Reasons for using MT707
The primary function of an MT 707 is to adjust a documentary credit’s terms to align with changes in trade agreements or to correct errors. This flexibility is vital for adapting to evolving trade conditions, facilitating smooth transaction flows, and maintaining the integrity of trade financing operations. It allows parties to promptly address and implement necessary adjustments without needing to issue a new documentary credit.
Potential issues and advancements
Challenges with MT 707
- Complexity and compliance: Amendments require meticulous attention to detail to ensure compliance with international trade laws and regulations, adding complexity to trade finance operations.
- Operational risks: Incorrectly executed amendments can lead to disputes, delays, and financial losses, emphasising the need for accuracy and clarity.
- Adaptation to changes: Rapidly changing trade environments and regulations demand agility and responsiveness from all parties, posing challenges in maintaining up-to-date amendments.
Advancements impacting MT 707
- Digitalisation and automation: The adoption of digital platforms and automation technologies promises to streamline the amendment process, reducing the potential for errors and enhancing efficiency.
- Blockchain technology: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent framework for executing amendments, ensuring authenticity and non-repudiation while potentially reducing fraud risks.
- Integration with electronic documentation: The move towards electronic documentation in trade finance can simplify the amendment process, allowing for quicker adjustments and better traceability.
The structure of the MT 707 message is meticulously designed to cater to the dynamic needs of international trade finance, facilitating smooth and clear communication of amendments to documentary credits. Through its comprehensive format and strict validation rules, the MT 707 ensures that all parties remain informed and aligned on the terms of trade transactions.
The MT 707 is indispensable in international trade finance, enabling parties to adapt documentary credits to changing circumstances efficiently. While challenges exist, technological advancements are paving the way for more streamlined, secure, and effective amendment processes, promising to enhance the agility and resilience of global trade operations.
- More articles on SWIFT Messaging Types
- Messaging Types Resources















