Bonds

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContent
A bond is a form of guarantee provided by a bank to a party involved in an international commercial transaction. Bonds guarantee that if there is a failure by one party to fulfil the terms of a contract (for example, by failing to provide the goods or services purchased under its terms), the bond-holding party can “call” their bond and receive financial compensation from the bank.
Bond – Definition
Trade bonds are a globally accepted mechanism of trade financing which help to drastically reduce the risks of international trade. In particular, bonds are frequently used by exporters to guarantee their business activities when working with trade partners abroad. To secure the transaction detailed in the parties export contract, trade financiers will issue a bond on behalf of the exporter to their international buyer or, where appropriate, a counter guarantee to a bank in the buyers country. If the contract is not fulfilled to the standards detailed in its terms, the buyer can call the bond and receive compensation.
Bond Products
Although their names vary, bonds are generally used in four commercial situations to guarantee the performance of one party in a transaction according to the terms of the contract underpinning it.
First, bid bonds can be used in tendering processes to assure importers that any bidders will take up the contract they are bidding for if the importer awards it to them. These bonds usually reflect 2-5% of the value of the contract under tender; if the contract is not taken up, the bank providing the bond will provide the importer with compensation to the value of the bond and recover the amount from the exporter. This reassures importers that all exporters tendering for a piece of work are genuinely interested in taking on the work at the price they bid, and protects them from any loss should they fail to do so.
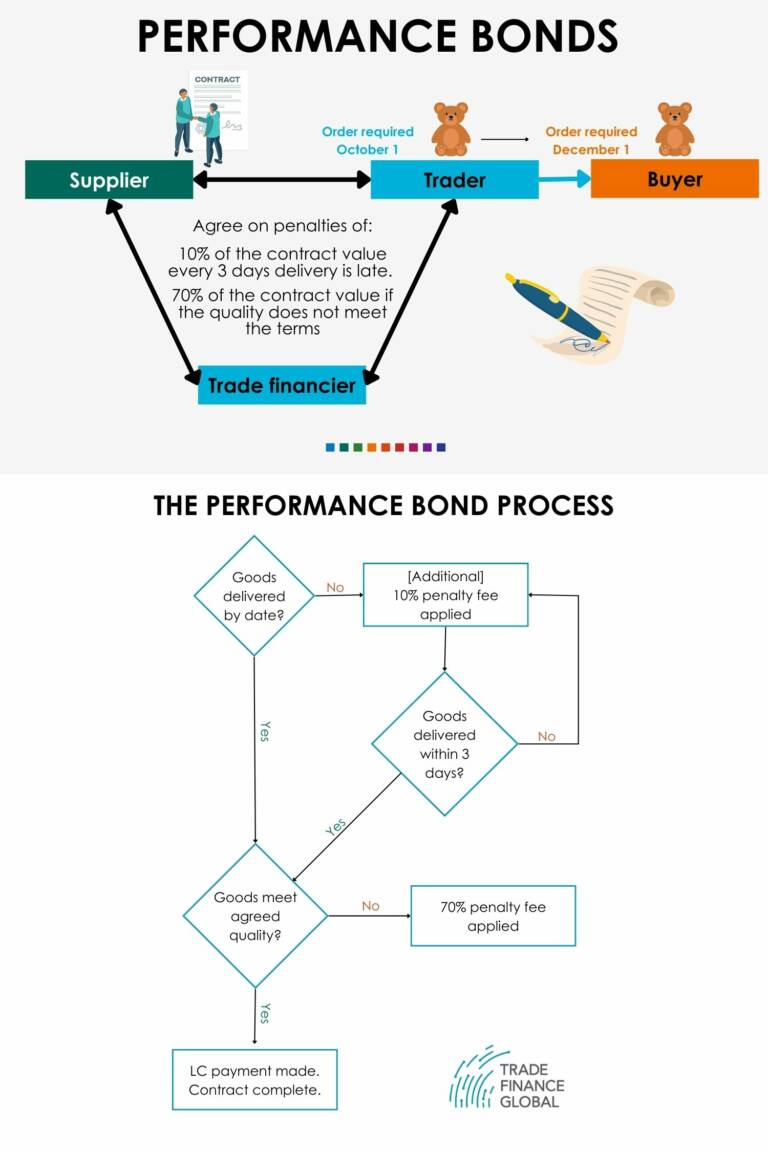
Second, bonds can be used to guarantee the quality of products purchased under contract. Called performance bonds, these bonds impose penalties of a stated percentage of the total contract price (often around 10%) on exporters who fail to export the right quantity or quality of goods purchased by an importer. However, these bonds are financial guarantees on the terms negotiated; whilst they provide the importer with a level of finance from the exporter, they do not guarantee that the bank will fulfil the contract (for example, by locating an alternative supplier) if the exporter fails to do so.
Third, importers are often requested to provide advanced payment to exporters prior to the completion of a contract to secure the exporters financial position or to provide cashflow for the firm to fulfil the order. If so, an advance payment bond can protect importers by undertaking that the exporter will refund any advance payment made by the importer in the event that the product is not delivered to the terms of the contract. Rather than a percentage, the value of these bonds are usually agreed in advance and paid immediately on demand if called.
Finally, once a transaction has been completed, importers sometimes wish to withhold full payment of the contracted amount for a given period of time. These are often required when an exporter has sold an importer some machinery, either to provide a warranty period to assure the purchased goods’ effectiveness, or to ensure that the exporter fulfils a promise to maintain or service the good for an agreed period. If so, warranty bonds or maintenance bonds can guarantee these obligations.
Example of How Bonds Work
- Funtime Traders is a wholesale toy merchant who imports toys and games into the UK from several East Asian manufacturing companies. They then run two businesses; their day to day wholesale business trading into small independent toy sellers, and one-off large contracts with major retailers.
- A large UK retail client approaches Funtime Traders with a request for a large one-off order of teddy bears at a fixed price. They want the teddy bears delivered to their distributor by December 1st so they can be in stores in the second week of December as part of a large pre-Christmas promotion on toys and games. Funtime Traders agree to attempt to source the product.
- Funtime Traders arranges with an existing supplier in China for the required quantity of teddy bears to be manufactured and shipped by October 1st, to allow six weeks for the goods to be shipped from China and two weeks contingency for any issues with customers or UK freight transportation.
- Because of the financial and reputational risk to Funtime Traders, if the goods are not shipped on time, they negotiate a performance bond between themselves and TFG. In the event of a delay, TFG agree to apply a financial penalty of 10% of the value of the contract to the Chinese supplier for every 3 days the goods are overdue their shipping deadline and pay the value to TFG.
- Assured by the existence of the bond, the large retailer chooses Funtime Traders as its supplier for the deal.
- The teddy bears are produced and shipped to the UK by October 1st, so a letter of credit is extended to the supplier paying them for the teddy bears.
- When the teddy bears arrive in the UK, their quality is confirmed, payments are exchanged, the contract is fulfilled and the bond expires.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Bonds
Bonds:
- Are a clear international format used by importers and exporters all over the world
- Are tailored to the specific value and risk a given contract poses to the buyer (i.e. with bespoke percentage thresholds agreed in advance)
- Protect exporters from loss of finance on contracts due to decisions taken by the buyer
- Can lower the cost of trade finance by providing security to investors
- Have lengthy time extensions to cover the immediate transaction and the continued terms of any given commercial contract (for example, a warranty bond)
Publishing Partners
- Risk & Insurance Resources
- All About Risk & Insurance Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences














