
Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContent
Project finance is the financing of long-term infrastructure, industrial, energy and public service ventures based upon non- recourse loans or limited recourse financial structure’s where venture debt and equity used to finance the project are paid back from the cash flow generated by the venture itself. Project finance is used to finance a project in sequential stages; it is highly useful for larger sized projects where the main characteristic of project finance is that the aggregate amount is not invested upfront through the securing of loans against the equity of sponsors.
The investors and sponsors can be split into thirteen parties with each party providing a financial service at different stages, accordingly the first party is the equity investor [typically the sponsor], the lenders including mezzanine financing, off-taker(s), contractor and equipment supplier, operator, financial advisory, technical advisory, legal advisory, loans, equity investors, regulatory agency, export credit agencies, insurance providers and hedge providers. Furthermore, documentation can be typically segmented into shareholder, project, finance, security, promotion and other documentation.
How is Project Finance Structured?
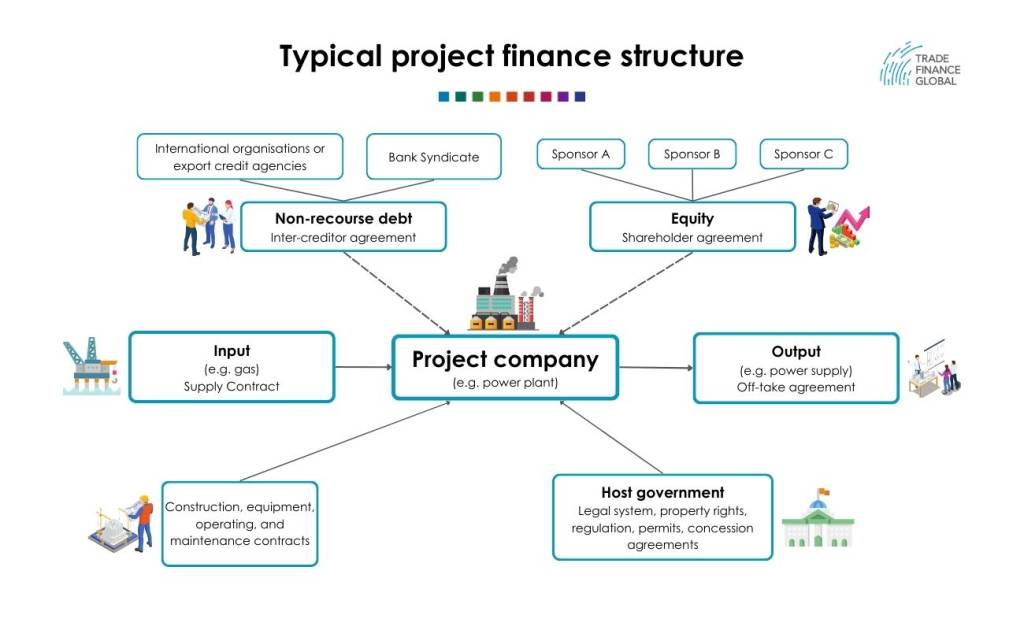
An illustrative overview of the structure of project finance as well as the connections between parties throughout the process. It is notable that everything is connected at the liability of the company rather than to the individual parties.
Project finance is associated with various advantages such as the opportunity to distribute risk [risk sharing], debt capacity extension and maintaining competitive leverage. The principle advantage is the avoidance of corporate repayment guaranteeing through the structure permitting the sponsor to finance the project off of another entity’s credit through contractual commitment. The basic structure of project finance forces sponsors to spread the risk through a network of security arrangements, contractual agreements and other alternative supplemental credit support to other financially capable parties willing to assume the risk for the venture, this significantly helps in the reduction of risk exposure to the project company.
The project finance route also authorizes the providers of funds to decide on how to effectively manage the remaining free cash flows [whether to reinvest or pay dividends] hence also significantly reducing conflict of interest between investor > management parties.
Companies seeking an entry route through project financing will be significantly challenged depending on whether they use equity or debt financing. Because of the associated difficulty and complications, on the contrary, it is not impossible either; concerning debt financing which is relatively more easier, it will in most depend on variables such as the sponsor’s impartiality and the value of collateral which the loan will be backed by. The decision will be made by financial institution[s] which will develop a financial model as a tool to process a comprehensive list of input assumptions and to provide outputs that reflect the anticipated real-life interaction between data and calculated values for the particular project, the bank will use numerous financial models, present + future valuations as well as formula’s such as sensitivity analysis to quantify and determine the optimal risk of issuing the loan[s]. The bank and the equity investors and sponsors of the venture will be in constant consultation with each other, correspondingly equity investors and sponsors can also provide financial models to the financial institution[s] in terms of negotiation and promotion.
Equity financing which is less conventional is a method of project finance that involves selling ownership of the company in exchange for sharing future profits of the venture. Equity financing is executed through a venture capitalist and/or equity crowdfunding [ownership is split into smaller shares to be sold to a diverse amount of investor], there are many advantages of equity financing such as GreatFont, the avoidance of steep interest rates and accelerated growth, however the disadvantages are the loss of complete ownership and difficulty in obtaining this sort of finance. The term “angel investors” has been coined for venture capitalists, unlike debt financing, equity financing is well suited for startups in high growth sectors, it also requires strong networks, business plans and stable financials to reinforce medium – long-term profitability.
To execute the entire venture fluidly, a special purpose entity is developed to support the entire venture, project finance works this way, it is fundamentally important that all parties are forefront when dealing with each other to avoid complications and bottlenecks. Companies such as Trade Financing Global provide advisory and consultancy professionals to construct financial models and technical negotiations on behalf of the venture to the financial institution acting as a mediating partner between equity investors and the financial institution, Trade Financing Global facilitates the most optimal financial solutions for clients seeking complex finance. It is important to ensure that ownership is held at 51% if the venture company is above 49% sold, ownership can become volatile and investors can potentially remove the original founder from leadership if they find it necessary. Insurance and Reinsurance are also incorporated into many venture financing to ensure security and regulation compliance.
Project Finance Security is highly important, there are market risks, construction + completion, exchange rates, conflicts with lender[s], technical, environment and political etc.., these are managed through licenses and long-term contracts that legally bind parties together for medium-long term. For instance, concerning an energy project, fuel supply would be arranged to have a 25-year agreement to provide a certain type of coal, international loans are hedged, concession agreements are provided by the government etc…
Conclusively, project financing is a loan structure that relies primarily on the ventures cash flow for repayment, with the venture’s assets, rights and endeavours held as secondary security [collateral]. Proactive communication between all parties as well as data integrity are key to securing a successful finance for the venture.
Referencing
APM Group, [2018], Benefits and Limitations of Project Finance, APMG International
https://ppp- certification.com/ppp-certification-guide/5-project-finance-—-benefits-and-limitations, retrieved 22/08/2018.
Marbury, [2014], Infrastructure Project Finance, National Institute of Banking and Finance [NIBAF], retrieved 22/08/2018.
Padhy, [2018], Getting into Project Finance, Wall Street Mojo,
https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/how- to-get-into-project-finance/, retrieved 22/08/2018.
A.C. Uzialko, [2018], Debt vs. Equity Financing, Business News Daily”, https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6363-debt-vs-equity-financing.html, retrieved 22/08/2018.
Hao, M. Wei, [2018], Project Finance Security Structures. Bank of China, www.asianeximbanks.org/sites/default/files/session5.pdf, retrieved 22/08/2018.
Our trade finance partners
- Export Finance Resources
- All Export Finance Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences




















