What Is Bill of Lading? BoL Guide & Example

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContents
What is a bill of lading?
In international trade, the bill of lading (BoL), often referred to as BL or B/L, is used when shipping goods from supplier to buyer.
The BoL is a legal document that provides multiple functions to make shipping more secure.
What are the functions of a bill of lading?
- A receipt confirms the goods have been transferred to the carrier (shipping company). Before shipping the goods, the carrier (shipping company) will check the description of the goods and sign the bill of lading.
- Evidence of the contract to undertake delivery of goods.
- Document of title (indication of ownership over goods).
The BoL describes the origin and destination of the goods, the quantity, and the description of the goods and shipping costs. Click here for some examples of what a bill of lading looks like
The BoL will also include INCOTERMS, if you need help take out a look at our guide to INCOTERMS.
Why are bills of lading used?
Bills of lading come into use when goods are moving and a transfer of title happens. Therefore they are used as a receipt; which is issued by the carrier when the product has been loaded onto a vessel.
The BoL is used as proof of shipment. This is particularly important for use in the customs process, insurance, and financial instruments. It is also used as commercial proof to show agreements have been fulfilled.
For example in a Letter of Credit (LC), normally the supplier must send the BoL to their advising bank which will send it to the buyer issuing bank which will be accepted or rejected by the buyer before the payment is made. The BoL is also required by the buyer to present to the shipper to receive the goods.

How are bills of lading transferred?
The BoL is transferred by endorsement or by lawful transfer of possession. A carrier must issue a bill of lading to the shipper which sets out the description of goods being shipped. The consignee should have received one of the BoLs so that when the goods arrive at the port they can’t be given to the shipowner to receive goods.
The buyer is often referred to as the consignee, and the supplier is often referred to as the shipper, with the carrier normally being the shipping company that is delivering the goods.
Why are there 3 bills of lading issued?
The traditional number is three; as one will be taken by the shipper, the consignee, and the other is usually taken by the lender or another party. It is not always the case that three bills of lading are issued; the number used is stated on the bill. However, it is preferred to have fewer BoLs; as the increased number creates a higher chance of releasing goods to the wrong party and fraud.
What are the types of bills of lading
1. Onboard bill of lading
Depending on the contract with the buyer or other requirements to meet standards for finance or insurance, the carrier may need an onboard BoL. This notifies that the goods are on board the ship (not just in port).
2. Clean bill of lading:
Indicates the goods have been checked and when left with the shipper had no discrepancies to the description of goods. This is very important for letters of credit (LC), the clean BoL is a declaration that the goods in the shipment are up to the standard described in the LC.
3. Claused bill of lading:
If goods are damaged, the carrier issues a claused bill of lading noting the level and quantity of goods that have been damaged. The consignee has the ability to reject the shipment upon arrival.
4. Straight bill of lading:
If a supplier is shipping directly to a buyer who has paid in advance. Only the consignee, in this case, the buyer, can sign the BoL. Therefore the BoL cannot be amended (destination or ownership).
We usually see bills of lading classed in two areas; being a straight BL and a to order BL. A straight BL is issued in favour of a specifically named consignee; which is not negotiable.
Conversely, an order BL is where there is no specific consignee; which is outlined on the document. Thus, this type of BL can be transferred or negotiated to be in favour of another party.
There is also the Switch Bill of Lading – read our article here which describes what a switch BL is.
Examples of Bills of Lading
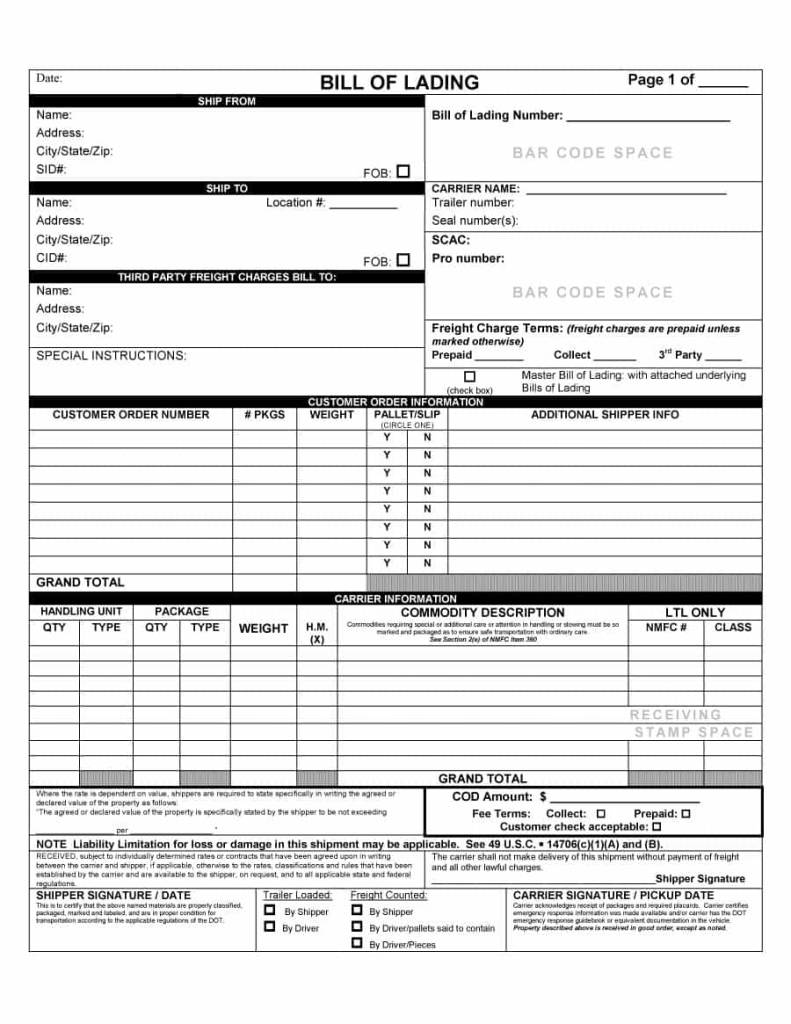
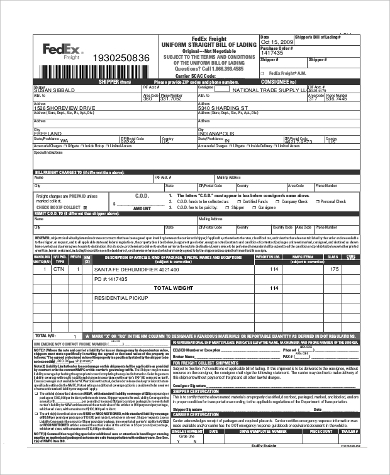

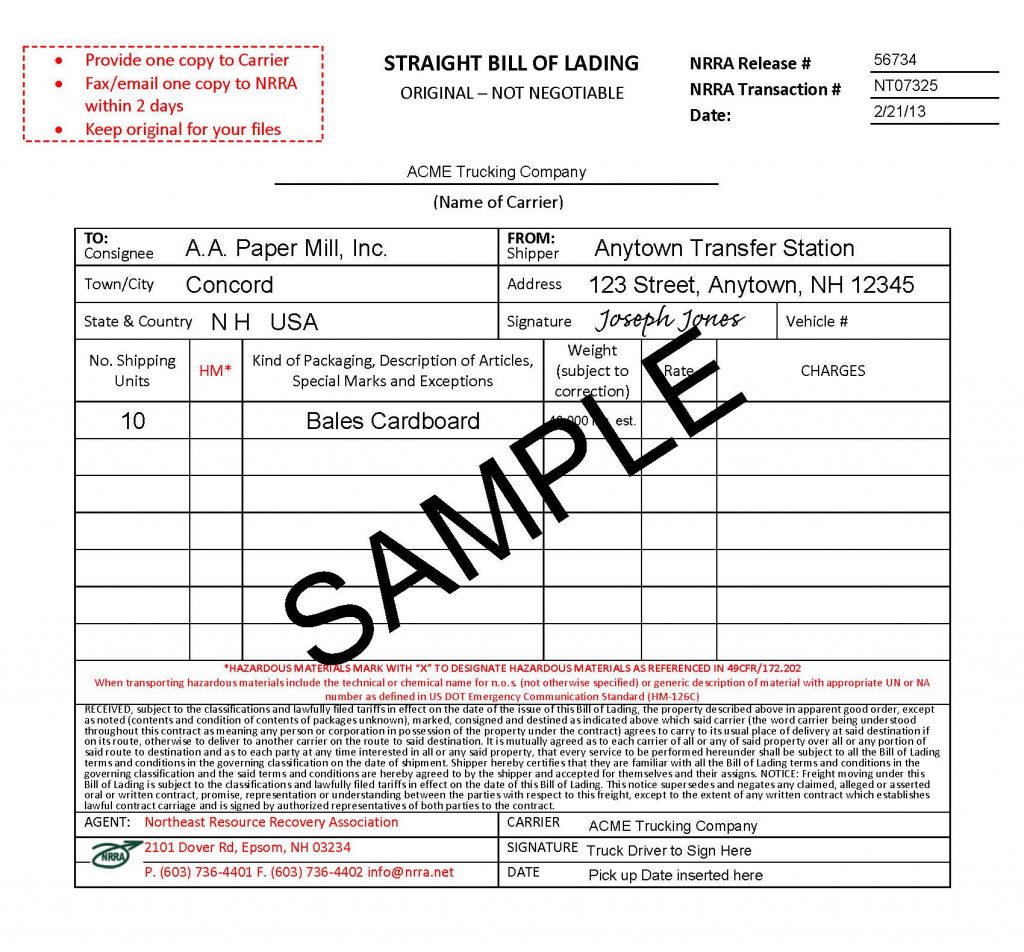
Charges for bills of lading
The BoL is usually paid by the carrier of goods. In 2022, Container-xChange, a logistics company, suggests that the charges range but start from USD 5 to USD 20.
Electronic bills of lading
Electronic bills of lading are becoming recognised in some jurisdictions as equivalent and fulfilling the role of paper bills of lading. For this to be successful the eBL has to reflect the function of the paper BoL.
- Confirmation that goods have been transferred to ship.
- Evidence of the contract for shipment of goods.
- Document of title, for the lawful transfer of ownership.
Notably, Singapore by accepting the UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR) and adapting some Singapore legislation has opened up to using eBLs.
In the UK, the law commission for England and Wales released a report and draft legislation in March 2022 on electronic transferable records (ETR) which includes eBLs. The recommendations build a framework for assessing the reliability of an ETR, the ability to identify the party that is in control of an ETR at one time, and the transferability of an ETR such that the previous owner is unable to change this.
Furthermore, an agglomeration of leading institutions in the trade space is looking to standardise the use eBLs. They are working to build adoption and acceptance by regulators, banks, and insurance companies.
These are positive first steps, however, still very few jurisdictions have adopted a legal framework that accepts eBLs, so the volume of trade using eBLS is still low. Nonetheless despite the expected slow takeup, trade digitisation initiatives will eventually snowball and this will include in these eBLs.
Benefits
- Lower administrative costs, of paper and admin in sending the paper BoL.
- Better speed and security when transferring and amending eBLs.
Issues:
- The key functionality of a BoL is that it is a ‘document of title’, most jurisdictions do not accept eBLs as ‘document of titles’ so are not used in traditional insurance or financial instruments.
- Low interoperability remains an issue, due to the low uptake by stakeholders and legal frameworks mean that they haven’t built systems to facilitate of eBLs. This will continue unless legal frameworks reform to recognise ETRs, which is a long process.
Testimonial
An example of when a bill of lading may be used is where there is a shipment across two countries. Bills of lading are used and forwarded onto the end buyer or offtaker. It may be the case that payment is only made when the original or copy bills of lading are received by the end buyer or lender They are used as a receipt of the shipment, confirmation of the underlying goods and to show the passing of title. – John B, Metals Trader
Case Study

Metals Distributor
Trade Finance Global along with their partner funders assisted us by clearly explaining how a new financing structure worked. This was when we were working on a shipment of metals travelling from Singapore to India. They clearly set out the documents that were to be sent by the supplier to us (as the buyer). This included the purchase order, packing list and bills of lading. The lender also had to receive these documents and would only make payment upon their receipt. However, in relation to the bills of lading, they would make payment upon receiving the copies of these documents.
- All Topics
- Key Terms
- Incoterms Resources
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences















